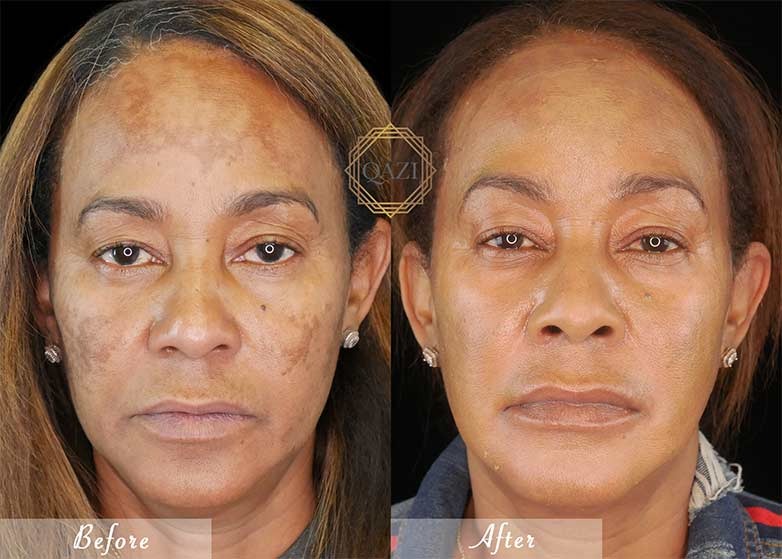
Hyperpigmentation disorders such as melasma, post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, and sun-induced dark spots are among the most common concerns in dermatology. Hydroquinone 4% remains one of the most studied and effective topical agents for reducing excess skin pigmentation when used correctly and under guidance.
This article explains how hydroquinone works, when it is recommended, and what results patients can realistically expect.
What Is Hydroquinone and How Does It Work?
Hydroquinone is a topical depigmenting agent that works by inhibiting tyrosinase, an enzyme essential for melanin production. By reducing melanin synthesis, hydroquinone gradually lightens hyperpigmented areas and evens skin tone.
Its main effects include:
- Reduction of melanin production
- Gradual fading of dark patches
- Improved skin tone uniformity
- Enhanced results when combined with sun protection
Hydroquinone does not bleach the skin instantly; visible improvement typically occurs over several weeks.
When Dermatologists Recommend Hydroquinone 4%
Hydroquinone 4% is commonly prescribed for:
- Melasma
- Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation
- Sun-induced dark spots
- Uneven skin tone resistant to cosmetic products
It is generally used for short- to medium-term treatment rather than continuous long-term application.
According to PubMed, hydroquinone remains the gold standard topical therapy for hyperpigmentation, with extensive clinical evidence supporting its efficacy and safety when used appropriately.
How to Use Hydroquinone Safely
Proper application is critical to achieving good results and avoiding side effects.
General guidelines include:
- Apply once or twice daily to affected areas only
- Avoid application on normal surrounding skin
- Use broad-spectrum sunscreen every morning
- Limit continuous use to recommended treatment cycles
Sun exposure without protection can worsen pigmentation and reduce treatment effectiveness.
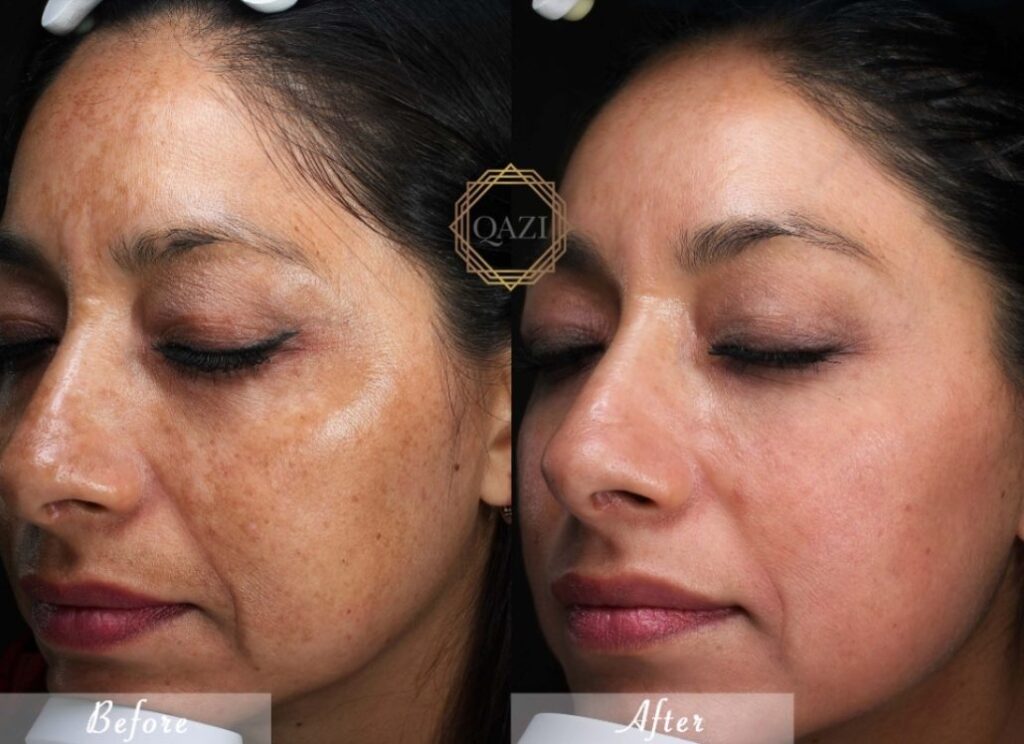

Possible Side Effects
Most users tolerate hydroquinone well, but potential side effects include:
- Mild irritation or redness
- Temporary dryness or peeling
- Rare cases of ochronosis with prolonged misuse
Using the correct concentration and following recommended treatment duration significantly reduces risks.
Choosing a Hydroquinone 4% Product
Product quality and formulation consistency are important for predictable outcomes. A commonly used medical-strength option is:
👉 hydroquinone 4% cream
https://okdermo.com/product/4-hydroquinone-cream-melalite-30g/
This concentration is widely used in clinical practice for managing moderate to severe hyperpigmentation.
Who Should Avoid Hydroquinone?
Hydroquinone may not be suitable for:
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women
- Individuals with very sensitive or damaged skin
- Patients unwilling to use daily sun protection
Dermatological consultation is recommended before starting treatment.
Conclusion
Hydroquinone 4% remains one of the most effective topical treatments for melasma and other forms of hyperpigmentation. When used correctly, it can significantly improve skin tone and reduce dark patches.
Successful treatment depends on proper application, sun protection, and realistic expectations regarding treatment duration and maintenance.